Classical and operant conditioning play a significant role in the world of business and understanding the psychology of human behavior. play pivotal roles in shaping consumer behavior, employee motivation, and marketing strategies. In this article, we delve into the concepts of classical and operant conditioning from a business perspective, exploring their applications, implications, and real-world examples.

Introduction: The Psychology Behind Business Success
In the fiercely competitive world of business, understanding human behavior is a game-changer. Successful businesses recognize the power of psychology in shaping consumer preferences, employee performance, and brand loyalty. Classical and operant conditioning are two psychological concepts that every business owner, marketer, and manager should comprehend.
Classical Conditioning: The Basics
Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
Classical conditioning, famously demonstrated by Ivan Pavlov’s dog experiment, is about pairing a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to create a conditioned response. In the business context, this can be seen in the association of a brand with positive emotions.
Pavlov’s experiment involved ringing a bell (neutral stimulus) before presenting food (unconditioned stimulus) to dogs. Over time, the bell alone triggered salivation (conditioned response) in the absence of food. Similarly, businesses can condition consumers to associate their brand with positive feelings through repeated exposure.
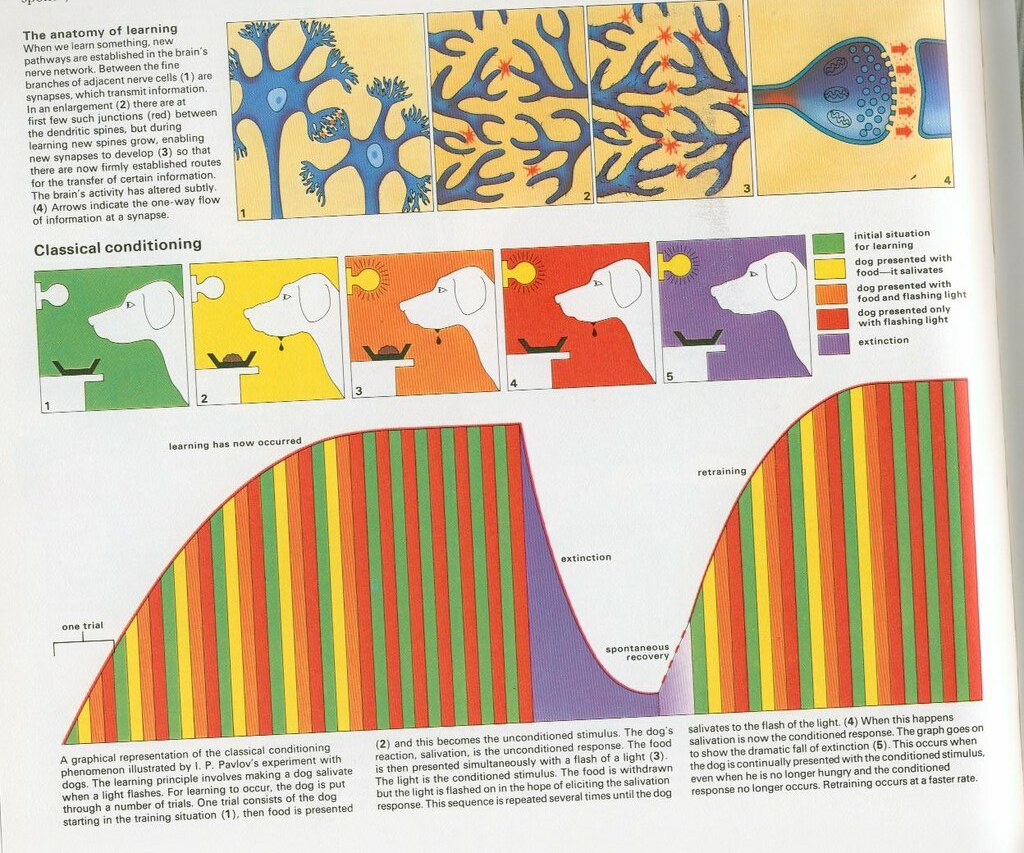
Business Applications
Classical Conditioning:
- Brand Recognition: One of the primary applications of classical conditioning in business is branding. Companies use logos, colors, jingles, and slogans to create positive associations with their products or services. Over time, consumers come to associate these elements with specific emotions or experiences. For instance, when you see the golden arches of McDonald’s, you may immediately think of fast food and convenience.
- Emotional Connection: Classical conditioning helps businesses establish emotional connections with their customers. By consistently delivering positive experiences, companies can condition consumers to associate their brand with trust, happiness, or other positive emotions.
- Product Launches: When introducing a new product or service, businesses can use classical conditioning to link it with their existing successful offerings. This association can make consumers more willing to try the new product, as they already have a positive perception of the brand.
Operant Conditioning:
Operant conditioning, developed by B.F. Skinner, focuses on modifying behavior through rewards and punishments. In the business world, this principle is crucial for motivating employees and driving desired outcomes.
- Employee Motivation: Businesses frequently use operant conditioning to motivate employees. Offering rewards such as bonuses, promotions, or recognition for achieving specific goals or targets encourages employees to perform at their best. Conversely, implementing penalties for undesirable behaviors can serve as a deterrent.
- Employee Training: In the context of employee training and development, operant conditioning plays a significant role. Employees receive feedback and reinforcement based on their performance, shaping their behavior and skills over time. Consistent positive reinforcement can lead to improved job performance and productivity.
- Customer Behavior: Operant conditioning can also be applied to influence customer behavior. Loyalty programs that offer rewards for repeat purchases, referrals, or reviews are a common example. Customers learn that certain behaviors lead to benefits, and this conditions them to engage more with the business.
However, Classical and Operant Conditioning could be different as per following ways…
The key difference between classical and operant conditioning in business lies in their focus and outcomes:
- Classical Conditioning is primarily concerned with creating emotional associations and brand recognition. It’s about linking a neutral stimulus (e.g., a logo) with positive emotions or experiences.
- Operant Conditioning, on the other hand, focuses on shaping behavior and performance through rewards and punishments. It’s about motivating employees, influencing customer behavior, and improving job performance.
In summary, both classical and operant conditioning are powerful tools in the business world. While classical conditioning creates emotional connections and brand loyalty, operant conditioning modifies behavior, motivates employees, and shapes customer behavior. Successful businesses often use a combination of these psychological principles to achieve their goals and foster growth.
Determining which conditioning method to use depends on the desired outcome. Classical conditioning is effective for creating emotional connections with a brand, while operant conditioning is ideal for modifying employee behavior and performance.
The concept can better be understood by following video depicting the difference between Classical and Operant conditioning:
Case Study: Coca-Cola’s Branding Success
Coca-Cola’s iconic red and white colors, paired with catchy jingles and heartwarming holiday commercials, exemplify the art of classical conditioning in marketing. The brand has successfully conditioned consumers to associate its products with joy and togetherness.
The Future of Classical and Operant Conditioning in Business
As technology advances, businesses will find new and innovative ways to apply conditioning principles. Virtual reality, personalized marketing, and AI-driven employee training are just a glimpse of what the future holds. The Classical and Operant conditioning can contribute to the future in following ways:
- Personalized Conditioning: As businesses increasingly leverage data and AI technologies, conditioning approaches will become more personalized. Companies will use sophisticated algorithms to tailor rewards and incentives to individual employees based on their preferences, performance, and career goals. This personalized approach will maximize motivation and engagement.
- Gamification and Digital Platforms: Gamification, the use of game elements in non-gaming contexts, will play a more prominent role in employee conditioning. Businesses will create digital platforms and apps that incorporate gamified elements to make conditioning more interactive and enjoyable. Employees will earn points, badges, and rewards for achieving specific goals and milestones.
- Behavioral Analytics: The use of behavioral analytics will become more prevalent. Businesses will employ advanced analytics tools to track and analyze employee behavior and performance data. This data-driven approach will enable companies to refine their conditioning strategies and make data-backed decisions on rewards, recognition, and training programs.
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development: With the rapid pace of technological advancements, continuous learning and skill development will be crucial for businesses to stay competitive. Conditioning efforts will focus on promoting a culture of continuous learning, where employees are encouraged and rewarded for acquiring new skills and knowledge.
- Remote Work and Flexibility: The rise of remote work and flexible work arrangements will reshape conditioning practices. Companies will need to find innovative ways to condition and motivate remote employees. Virtual team-building exercises, online recognition programs, and flexible rewards will become more common.
- Emphasis on Well-Being: Employee well-being will be a central consideration in conditioning strategies. Companies will prioritize not only performance but also the physical and mental health of their workforce. Conditioning efforts will include incentives for wellness activities, mindfulness programs, and stress management initiatives.
- Ethical and Inclusive Conditioning: Businesses will place a greater emphasis on ethical conditioning practices. Conditioning efforts will align with principles of diversity, equity, and inclusion. Companies will reward behaviors that contribute to a more inclusive workplace and discourage discrimination and bias.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, understanding and harnessing the power of classical and operant conditioning is a strategic advantage. By creating positive associations, motivating employees, and building strong brand loyalty, businesses can thrive in a competitive world where psychology and consumer behavior play pivotal roles.
FAQs
- How can classical conditioning be used in employee training?
- Are there ethical concerns associated with operant conditioning in business?
- What are some real-world examples of businesses using conditioning to their advantage?
- How do businesses measure the effectiveness of conditioning strategies?
- What is the role of reinforcement schedules in employee motivation and performance?


2 thoughts on “Classical and Operant Conditioning: The Power of Psychology in Business Growth.”
Comments are closed.